Composition and application of PP and PE raw materials and flame retardants of halogen-free flame retardant polyolefin power cable materials
 Date:2022-05-09
Date:2022-05-09 Views:1392
Views:1392
Application status of halogen-free flame retardant polyolefin power cable materials
preface
With the rapid development of domestic economy, the demand for wires and cables in power, construction, communication and other industries is increasing, and the output of polyolefin cables shows an unprecedented exponential growth trend. It is expected that by 2024, the demand for wires and cables in China is expected to exceed 1.9 trillion yuan, with an annual compound growth rate of about 4%. The market demand for halogen-free flame retardant wire and cable materials is about 200kt. It is expected that in the next 3-5 years, The demand for this kind of cable will increase at a rate of about 10%. By 2025, the demand for halogen-free flame retardant wire and cable materials will reach about 350kt. Polyolefin materials commonly used in cables have relatively high flammability, are easy to decompose and burn at high temperature, and produce a large number of molten droplets during combustion, which ignite other combustibles, expand the scope of fire, and bring serious casualties and huge economic losses. Therefore, the flame retardant research of polyolefin cable has always been a hot spot.
Polyolefin flame-retardant cable material is the flame-retardant modification of cable insulation material and sheath material through flame-retardant additives. Polyolefin base materials used for flame retardant cables shall meet the following requirements: (1) have good electrical, mechanical and processing properties; (2) It is beneficial to increase the filling amount of flame retardant additives.
Additives used for flame retardant cables shall meet the following requirements: (1) they have flame retardant properties; (2) Reduce the smoke emission and toxicity of polyolefin cable materials; (3) Maintain the electrical, mechanical and processing properties of flame retardant cable materials.
Starting from the selection of polyolefin matrix material for halogen-free flame retardant cable, this paper analyzes the pyrolysis and flame retardant mechanism of polyolefin, discusses the types and flame retardant mechanism of flame retardant additives, and finally discusses the research status, advantages and disadvantages and specific application of flame retardant polyolefin cable material technology.
1. Selection of flame retardant cable base material
As the carrier of power transmission, the insulation performance and mechanical strength of cable are very important, and the cable matrix material directly affects the electrical and mechanical properties of cable material. The widely used polyolefin cable matrix materials are polyethylene and cross-linked polyethylene. In addition, the power cable material based on polypropylene is also the focus of research.
1.1PE
The non-polar group in the molecular structure of PE is a non-polar polymer material, while halogen-free flame retardants generally have strong polarity and poor compatibility with PE. Therefore, improving the polarity of PE cable base material or treating flame retardant additives with coupling agent to improve the filling amount and compatibility of halogen-free flame retardant is the key step to improve the flame retardant performance of PE. The common way to improve the polarity of PE base material is to blend and modify PE with polymers with strong polarity, including EVA, EEA and EPDM. On the one hand, the addition of these copolymers can introduce polar groups, improve the affinity between polymer matrix and inorganic flame retardant, increase the filling amount of flame retardant and improve the flame retardant performance of composites. On the other hand, these copolymers have good flexibility, toughness, environmental stress cracking resistance and bonding properties, especially the mechanical properties can be improved.
1.2PP
PP is widely used in wires and electrical equipment cables in various industries because of its excellent electrical properties, chemical reagent resistance and oil resistance. Generally, PP materials have poor toughness and impact resistance. Researchers have modified them by copolymerization, blending, grafting and nano addition, and the mechanical and electrical properties have been greatly improved. Compared with XLPE cable, the processing technology of modified thermoplastic PP is simpler and recyclable, which improves the cable production rate and greatly reduces the production cost. In addition, the temperature resistance grade of PP cable is higher than that of XLPE, which can significantly improve the cable ampacity and is highly expected in the field of power cables.
PP has high combustion heat and low carbonization rate. The main disadvantages of limiting PP as flame retardant cable material are its short molecular chain and high crystallinity, which lead to poor compatibility with flame retardant. A small amount of flame retardant will cause a significant decline in the processing and mechanical properties of PP. Especially when the cable needs to be bent, its bending resistance is also poor, which may cause mechanical damage in the process of transportation and laying. Therefore, on the premise of not affecting the mechanical properties of PP, improving its flame retardant properties has become a research hotspot of PP Flame retardant modification.
There are many modification methods of PP Flame Retardant base material, but it is the most effective way to modify it by CO mixing and copolymerization in the field of cable insulation. Blending modification refers to the blending of PP with other elastomers: PE, EVA and Poe. Copolymerization modification refers to the connection of ethylene or propylene molecular chain on the molecular chain of PP. These two methods have low cost, simple process and great technical flexibility, and have good development prospects at home and abroad.
2 types of polyolefin cable flame retardant
2.1 polyolefin combustion characteristics
The constituent elements of polyolefins such as PE and PP contain very high contents of C and h, so they are very easy to burn, the limiting oxygen index is only 17%, and melt droplets and casting fire are easy to occur in the combustion process. There are three stages in the process of polyolefin combustion: softening, decomposition and combustion. A large number of combustible substances will be produced in the decomposition process, and the heat released in the combustion process promotes the decomposition of polyolefin. Therefore, the flame-retardant mechanism of flame-retardant polyolefin cable materials is mainly reflected in the use of flame retardants to slow down the thermal decomposition of materials and limit heat transfer, so as to avoid fire. According to the composition of flame retardants, halogen-free flame retardants can be divided into phosphorus system, nitrogen system, silicon system, boron system, inorganic metal hydroxide and expansion type.
2.2 halogen free flame retardant
At present, nitrogen, phosphorus, boron and silicon flame retardants are commonly used in halogen-free flame retardant systems for power cables.
Nitrogen flame retardants are mainly melamine and its salts, which have high decomposition temperature. During combustion, they mainly produce non-toxic and non corrosive products such as NH3, N2, no and water vapor. Nitrogen flame retardants absorb a lot of heat and release non combustible gases through volatilization and thermal decomposition, which can greatly reduce the surface temperature of polymers and dilute the concentration of combustible gases and oxygen in the environment, and finally achieve good flame retardant effect. Nitrogen based flame retardants and other flame retardants have good synergistic effects. For example, in nitrogen phosphorus flame retardants, it can promote the carbonization of phosphorus based flame retardants, form an expanded carbon layer, and play a good role in heat insulation and flame retardancy. Some nitrogen flame retardants such as melamine cyanurate are often used as lubricants and compatibilizers to improve the blending of other flame retardants in polyolefins.
Phosphorus based flame retardants mainly use phosphorus groups to dehydrate and carbonize the polymer surface in the process of thermal decomposition, which plays the role of isolation and flame retardancy. Among them, ammonium polyphosphate (APP) is commonly used in the flame retardant system of power cables. The disadvantages of phosphorus containing flame retardants are that phosphorus has neurotoxicity, low stability, poor water resistance, poor compatibility with polymers and great impact on mechanical properties, so its application is limited.
The flame retardant mechanism of boron compounds is to form a glass isolation layer during combustion, which can block oxygen and volatile combustible gases, prevent further oxidation of carbon layer and promote carbon formation. Compared with phosphorus flame retardants, boron flame retardants have good thermal stability, low toxicity and low smoke, so they are more suitable for popularization and application. Zinc borate is commonly used as a flame retardant synergist, but its effect alone is not good. It is mainly used as a flame retardant synergist.
Silicon flame retardant is a new environment-friendly flame retardant, which has the characteristics of high flame retardant efficiency, low toxicity, anti droplet and smokeless. Inorganic silicon flame retardants are commonly used in power cable flame retardant, including silicate minerals, such as talc powder, layered silicate and porous silicate. They not only promote carbon formation in the combustion process, but also increase the absorption of flue gas.
2.3 inorganic metal hydroxide flame retardant
At present, the commonly used inorganic metal hydroxides are aluminum hydroxide (ATH) and magnesium hydroxide (MDH), which have the characteristics of low smoke, non-toxic and green environmental protection. As a new pollution-free flame retardant, they have attracted extensive attention. When the temperature of ATH and MDH is higher than 200 ℃, they begin to decompose and absorb a lot of heat to reduce the local temperature of the combustion area. The water vapor generated by their decomposition dilutes the concentration of combustible gas and oxygen. At the same time, the generated non combustible oxide forms an isolation film, which has the effect of flame retardant.
Inorganic metal hydroxides reduce the combustion heat by their own decomposition and dilute oxygen at the same time, so their flame retardant efficiency is low, and the content often exceeds 50%. At the same time, the polarity of inorganic metal hydroxide is large and its compatibility with polyolefin cable base material is poor, which makes it difficult to disperse in the processing process and easy to form mechanical stress points, which significantly reduces the mechanical properties of cable material. At present, the research on ATH and MDH as flame retardants still focuses on improving the compatibility. The common methods include particle refinement, surface modification and adding compatibilizers.
2.4 intumescent flame retardant
The intumescent flame retardant is mainly composed of phosphorus and nitrogen. It combines the advantages of the two flame retardants and has the characteristics of non-toxic and less smoke. After being heated, the phosphorus system material forms an isolation film, and the nitrogen system material decomposes into water and gas. Among them, the gas decomposed by the nitrogen system is conducive to the formation of foam like carbon layer of the phosphorus system. The foam like carbon layer can play the role of oxygen isolation and heat insulation, and can prevent molten drops at the same time. Compared with other halogen-free flame retardant systems, in the field of Flame Retardant PE and PP, when the content of IFR is 20% ~ 30%, it can achieve excellent flame retardant effect.
The theoretical phosphorus content of app is more than 31%, which is the most common acid source in IFR. At the same time, it also plays the role of gas source. However, APP used in PE and PP has many defects in performance, such as insufficient thermal stability, pungent smell and mold corrosion during processing; Poor compatibility with PE and PP, unable to meet the requirements of mechanical properties; Poor water resistance, high moisture absorption, etc. Therefore, surface modification of app is one of the effective ways to solve the above problems.
The surface modification of app can be divided into physical coating method and surface chemical modification method. The key of physical coating is that the coating material needs to have good compatibility with app to ensure firm coating; The coating material also needs to have good thermal stability, interfacial compatibility and good water resistance. Compared with physical coating, the binding force of chemical modification is stronger, but chemical modification will increase the use cost of app and raise the application threshold.
3 flame retardant technology of cable material
According to GB / t32129-2015 halogen free low smoke flame retardant cable materials for wires and cables, the modified PE and PP power cable materials shall meet the properties in Table
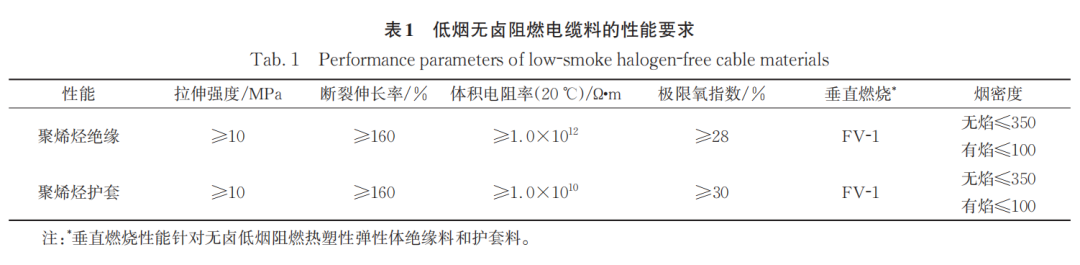
3.1 modified metal hydroxide flame retardant
Metal hydroxide is a widely used green flame retardant. Aiming at the disadvantages of poor mechanical properties and poor compatibility of its modified flame retardant cable material, researchers try to modify it to enhance compatibility and improve flame retardant efficiency. Taking MDH as an example, a coupling agent with both hydrophilic and lipophilic groups is used to modify its surface. The coupling agent connects metal oxides and polyolefins, which can improve the compatibility.
4 Conclusion
Polyolefin flame retardant cable material has good insulation performance. It is widely used in power cable insulation all over the world and has made an important contribution to power transmission. However, with people's attention to environmental problems, the use of halogen-free flame retardant instead of traditional halogen flame retardant is an important trend in the development of cable insulation.

 Wechat scanning communication
Wechat scanning communication